SIGAFD: A Smart IoT Gateway for Attrial Fibrillation Detection
-
START DATE
30 Oct, 2019
-
END DATE
29 Sep, 2020
DETAILS
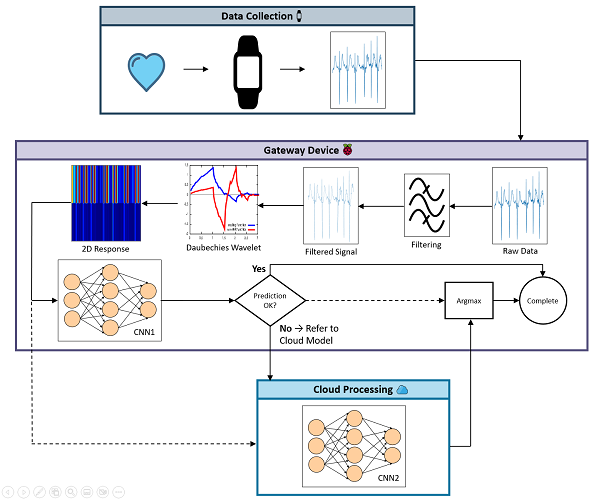
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a cardiac arrhythmia causing the heart to beat erratically. The most recent figures from the World Health Organization estimate that AF affects 33.5 million people globally. This project involves the development of a dual convolutional neural network (CNN) based AF detection system. The system runs mainly on an IoT gateway where preprocessing and predictions are made via a model designed for low-power devices. In difficult-to-determine instances, a backup model hosted on a cloud server is utilised. Local classification of AF reduces the overheads for cloud storage capacity and transfer of data. The proposed runtime system ultimately received an F1 score of 0.94 when evaluated using previously unseen data.
Students(s): Eoin Flanagan
Publications
- Flanagan, Eoin, and Robert Sadleir. “A Smart IoT Gateway Capable of Prescreening for Atrial Fibrillation.” In Internet of Things: 5th The Global IoT Summit, GIoTS 2022, Dublin, Ireland, June 20–23, 2022, Revised Selected Papers, pp. 111-123. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023.